When working on a 1978 Ford vehicle, having access to a detailed wiring diagram is crucial for understanding the electrical system. In this article, we will delve into the importance of 1978 Ford Wiring Diagrams, how to read and interpret them effectively, and how they can be used for troubleshooting electrical problems.
Why are 1978 Ford Wiring Diagrams Essential?
1978 Ford Wiring Diagrams are essential for several reasons:
- They provide a visual representation of the vehicle’s electrical system, showing how all the components are connected.
- They help in identifying the location of wires, connectors, and components, making it easier to diagnose and repair electrical issues.
- They serve as a guide for proper installation of aftermarket electrical accessories or upgrades.
How to Read and Interpret 1978 Ford Wiring Diagrams Effectively
Reading and interpreting wiring diagrams can be daunting for some, but with the right approach, it becomes much simpler:
- Start by familiarizing yourself with the symbols used in the diagram, such as lines, dots, and shapes representing various components.
- Follow the flow of the diagram from the power source to the components, noting the color-coding of the wires along the way.
- Pay attention to the key provided with the diagram, which explains the symbols and color codes used.
Using 1978 Ford Wiring Diagrams for Troubleshooting Electrical Problems
When faced with electrical issues in your 1978 Ford vehicle, the wiring diagram can be your best friend:
- Identify the affected circuit on the diagram and trace the wires to locate any potential faults, such as loose connections or damaged insulation.
- Compare the actual wiring in the vehicle to the diagram to see if there are any discrepancies that could be causing the problem.
- Use a multimeter to test the continuity and voltage along the circuit, following the diagram as a guide.
Importance of Safety When Working with Electrical Systems
Working with electrical systems can be hazardous, so it’s essential to prioritize safety:
- Always disconnect the battery before working on any electrical components to prevent the risk of electric shock or short circuits.
- Use insulated tools and wear protective gear, such as gloves and goggles, when handling electrical wiring.
- Avoid working on electrical systems in wet or damp conditions to prevent the risk of electrocution.
1978 Ford Wiring Diagram
1978 Ford F100 Wiring Diagram

1978 Ford Truck Wiring Schematic

1978 Ford F100 Wiring Diagram
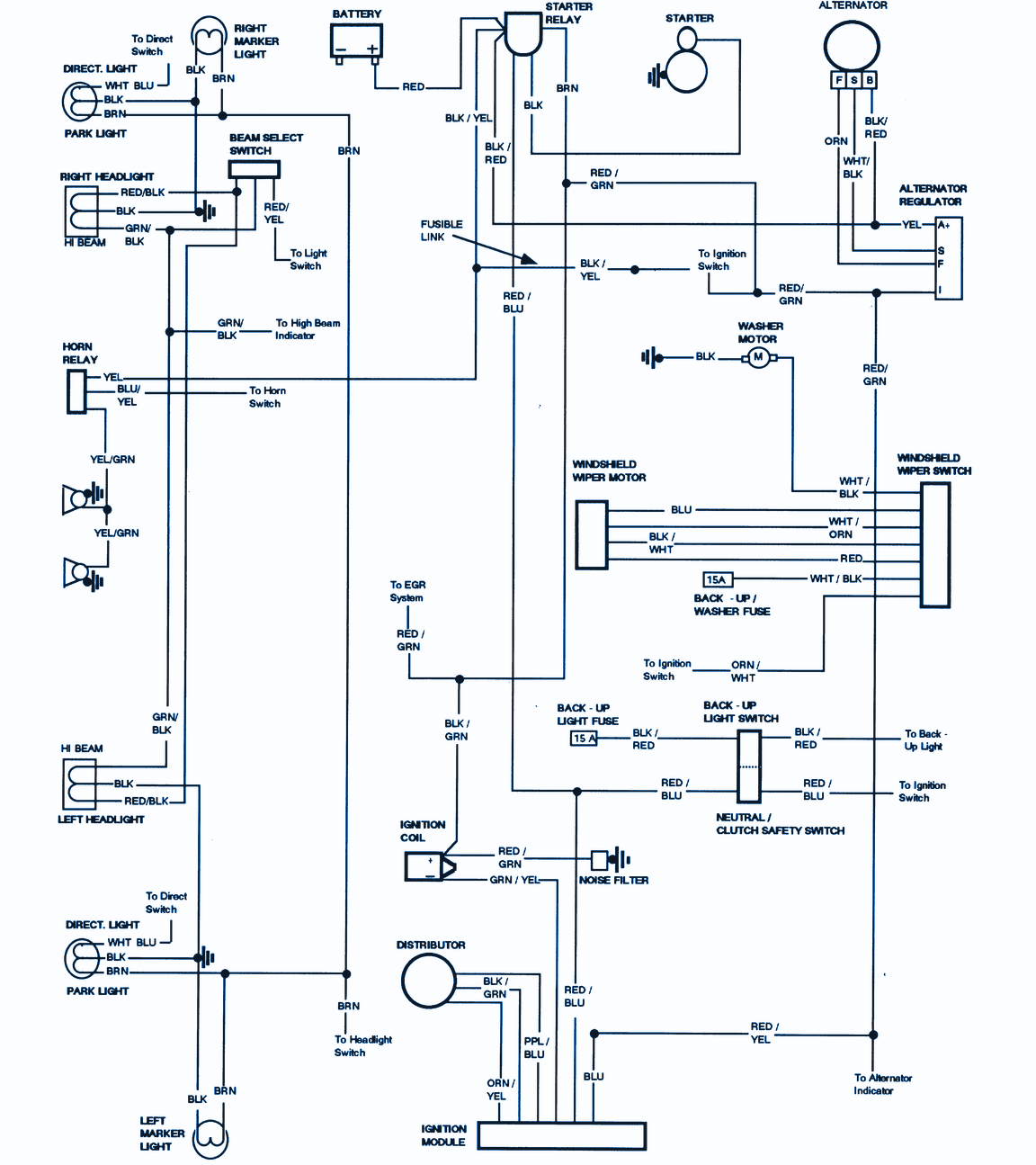
1978 Ford Truck Wiring Schematics

1978 Ford F150 Brake Light Wiring Diagram – Wiring Diagram

78 Ford Truck Wiring Diagram
