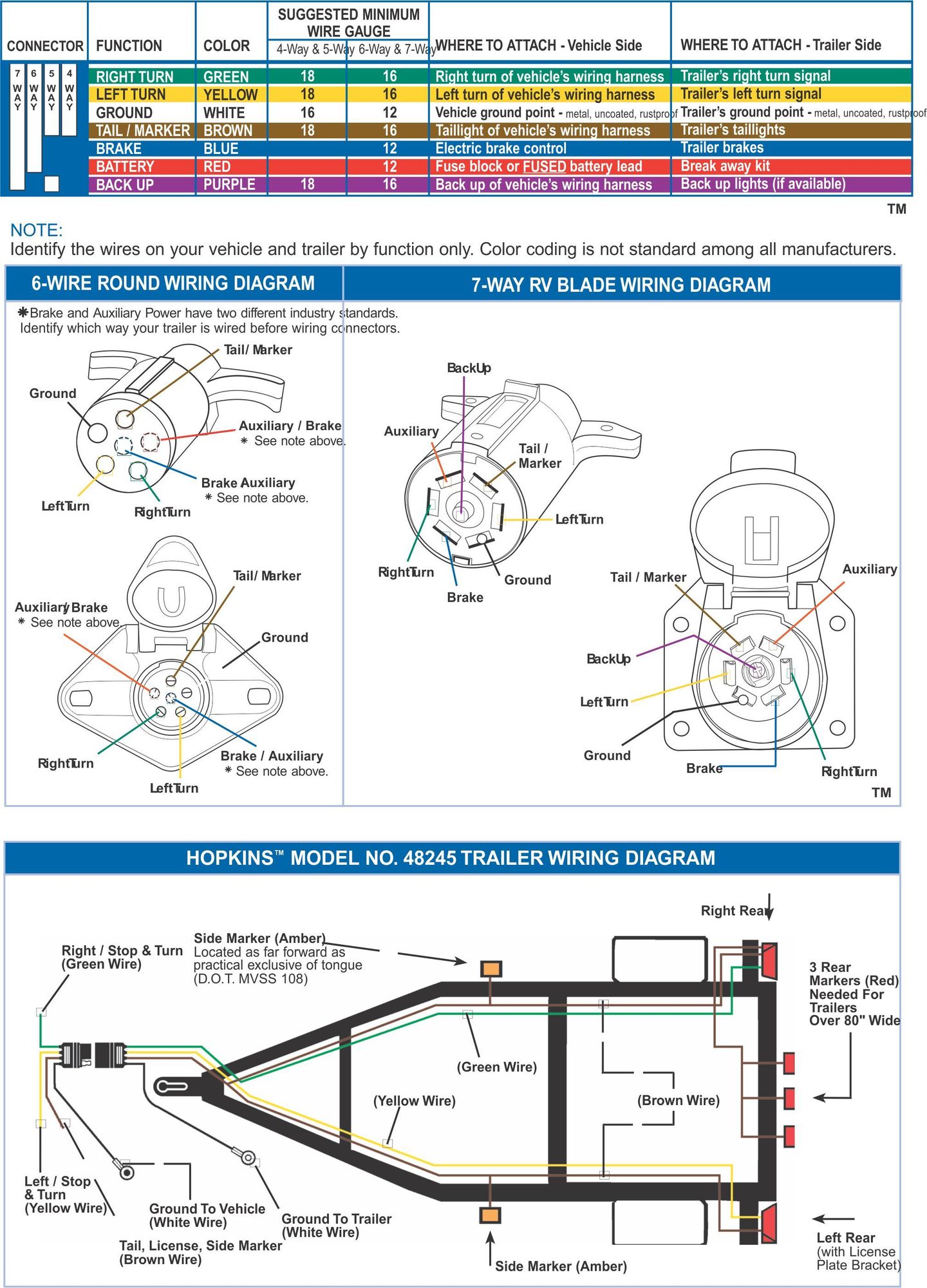
When it comes to ensuring the proper functioning of your Ford truck’s trailer wiring system, having access to a Ford Truck Trailer Wiring Diagram is crucial. This diagram serves as a guide that illustrates the electrical connections between the various components of the trailer wiring system, helping you to troubleshoot issues and make necessary repairs.
Why are Ford Truck Trailer Wiring Diagrams Essential?
- Provide a visual representation of the wiring configuration
- Help ensure proper installation of trailer wiring components
- Aid in troubleshooting electrical issues
- Ensure compliance with safety standards
How to Read and Interpret Ford Truck Trailer Wiring Diagrams Effectively
Reading and interpreting a Ford Truck Trailer Wiring Diagram may seem daunting at first, but with a bit of practice, you’ll be able to navigate the diagram with ease. Here are some tips to help you make sense of the diagram:
- Familiarize yourself with the key symbols and color codes used in the diagram
- Identify the components of the trailer wiring system and their corresponding connections
- Follow the flow of electrical current to understand how power is distributed throughout the system
Using Ford Truck Trailer Wiring Diagrams for Troubleshooting
When faced with electrical problems in your Ford truck’s trailer wiring system, a Ford Truck Trailer Wiring Diagram can be a valuable tool in identifying and resolving issues. Here’s how you can use the diagram for troubleshooting:
- Trace the path of the electrical circuit to locate potential faults or breaks in the wiring
- Check for loose connections or damaged wires indicated on the diagram
- Use a multimeter to test for continuity and voltage at various points in the system
Importance of Safety When Working with Ford Truck Trailer Wiring Diagrams
When working with electrical systems and using wiring diagrams, safety should always be a top priority. Here are some safety tips and best practices to keep in mind:
- Always disconnect the battery before working on the electrical system
- Use insulated tools to prevent shock hazards
- Avoid overloading circuits and use the appropriate gauge of wire for the job
- Double-check your work and test the system before putting it into use
Ford Truck Trailer Wiring Diagram
Ford Truck Trailer Wiring

Ford 7 Pin Trailer Wiring Diagram – Free Wiring Diagram

How to Wire Your Ford Truck Trailer: A Comprehensive Wiring Diagram Guide

1996 Ford F250 Trailer Wiring Diagram Pictures – Faceitsalon.com

ford trailer wiring diagram 6 pin

Trailer Wiring Diagram 2006 Ford Truck